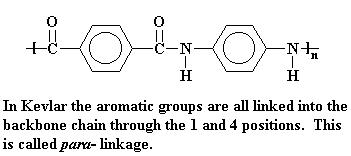It might be difficult for you to conjure up an image when I mention aramid fibers. Still, if I told you that they are the raw materials used within body armor, bullet-proof vests, firefighter uniforms, etc., you start to get the picture.
In fact, aramid fibers are the superstar family in the fiber world. They appear as bright golden-yellow filaments (so far, more colors are available). The name comes from a combination of two words, "aromatic polyamide." Due to their outstanding strength-to-weight ratio and heat-resistant properties, aramid fibers are widely used in the above-mentioned protective-wear applications.

But aramid fiber properties are more than that (more on those later on). Aramid fibers play an essential role in composites, the automotive industry, military applications, and many similar fields.
1. History of Aramid Fibers
It took quite a while to work out how to utilize aramid fibers, mainly because they just can't be dissolved in anything. This makes the process of working with aramid fibers rather tricky. The dramatic development of aromatic polyamides is mainly down to the discovery of lyotropic liquid crystalline aramid, which in solid form is commercially known as Kevlar® (DuPont's brand).
In the early 1970s, a Polish-American chemist named Stephanie Kwolek, a DuPont Research Scientist, invented the para-aramid, branded as Kevlar®. In 1964, Kwolek's team started looking into a new lightweight, strong fiber for tires. The discovery of lyotropic liquid crystalline aramids enabled her to develop a novel spinning process for the anisotropic solution, leading to Kevlar's commercialization.
Structure of Kevlar, a para-aramid
Kwolek's invention of Kevlar was fundamentally groundbreaking. In July 1995, she became the fourth woman to be added to the National Inventors Hall of Fame. In 1995 DuPont also awarded her the Lavoisier Medal for outstanding technical achievement, which is remarkable as she is the only female employee to have received the honor.

A Firefighter in Toronto, Canada wears a Nomex hood (2007)
However, aramid fibers themselves became commercialized in the early 1960s, before the invention of Kevlar. The trade name was Nomex®, a meta-aramid fiber produced by DuPont. The credit for this great invention goes to Dr. Wilfred Sweeny, a Scottish-born scientist who also worked for DuPont.
This particular fiber features excellent thermal resistance, which means that it does not melt or catch fire at a typical oxygen level. This material was very quickly used to manufacture protective clothing, and air filtration units, and became a substitute for asbestos. Nomex® was marketed in 1967 and has saved millions of lives, including firefighters, aircraft pilots, and racing car drivers, to name but a few!
Meta-aramids are produced in many other countries including the Netherlands, Japan by Teijin under the trade name Conex, in Korea by Toray under the trade name Arawin, in China by Yantai Tayho under the trade name New Star, by SRO Group (China) under the trade name X-Fiper, a variant of meta-aramid in France by Kermel under the trade name Kermel as well.
There are even more twists and turns in the development of aramid fibers which you can see in the table below, the entire history of aramid fibers.
Development of Aramid Fibers
| Year | Event | Producer | Base Polymer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1938 | Commercialization of Nylon | ||
| 1962 | Introduction of Nomex fiber | DuPont Co., USA | MPD-1 |
| 1965 | Discovery of anisotropic polymer | ||
| 1970 | Discovery of air-gap spinning | ||
| 1971 | Introduction of fiber-B | DuPont Co., USA | (i)PBA (ii)PPD-T |
| 1972 | Introduction of Tejincorex Commercialization of Kevlar Introduction of Twaron Introduction of Kermel Introduction of Fenilon |
Teijin Ltd, Japan & DuPont Co., USA Akzo Chemicals BF, Netherlands Rhone-Poulene, France USSR |
MPD-1 PPD-T PPD-T MPD-1 MPD-1 |
| 1976 | Introduction of SVM fiber(formerly Vniivlon) | USSR | Polyhetero arylene |
| 1978 | Development of arenka aramid fiber | ||
| 1987 | Introduction of HMO-50(Technora) aramid fiber | Teijin Ltd, Japan | |
| 1988 |
Commercialization of Twaron (formerly Arneka) Introduction of PBO-HM |
Toyobo. Japan Toyobo. Japan | |
| 1996 | Introduction of Trevar(discontinued later) | Hoecst. Germany | |
| 1997 | Kevlar 49 HS by new fiber technology(NFT) | DuPont Co., USA | |
| 1998 | Introduction of Armos | Russia | p-aromatic hydrocyclic copolyamide |
2. Categories of Aramid Fibers
In addition, both Nomex (a meta-aramid) and Kevlar (a para-aramid) have a number of variants each with specific properties.
For Nomex, its variations are of the copolyamide type, of which a well-known one is Teijinconex under Teijin.
For Kevlar, other para-aramid yarns can act as the replacement. They usually come at a lower cost, with Twaron and Technora by Teijin, Heracron by Kolon, as well as Alkex by Hyosung included, each of which can exhibit similar results to Kevlar.
Kevlar® and Para-aramid Filament Yarn Alternatives Compared
| Manufacturer | Dupont | Hyosung | Kolon | Teijin | Teijin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trade Name | Kevlar®29 | Alkex®AF-1000 | Heracron®HF200 | Twaron® | Technora® | |
| Specification | UofM | |||||
| Density | (g/cm3) | 1.44 | 1.44 | 1.44 | 1.44 - 1.45 | 1.39 |
| Tenacity | (g/den) | 23 | 23 | 23.0-24.0 | 18.7 - 28.3 | 28.3 |
| Modulus | (Gpa) | 70.33 | 70 - 102 | 8. - 109 | 60 - 120 | 74 |
| Elongation @ Break | (%) | 3.6 | 2.8 - 4.2 | 2.8 - 3.6 | 2.2 - 4.4 | 4.5 |
| Moisture Regain | (%) | 7 | 4.5 | not avail | 3.2 - 5.0 | 1.9 |
| Decomposition | (°C) | 427 - 482 | 500 | not avail | 500 | 500 |
| (°F) | 800 - 900 | 932 | not avail | 932 | 932 | |
3. The Molecular Structure of Aramid Fibers
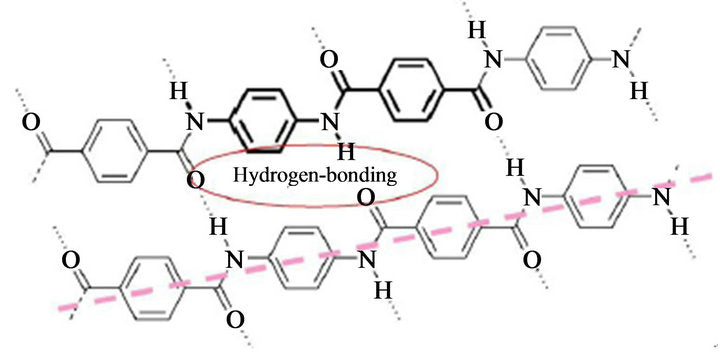
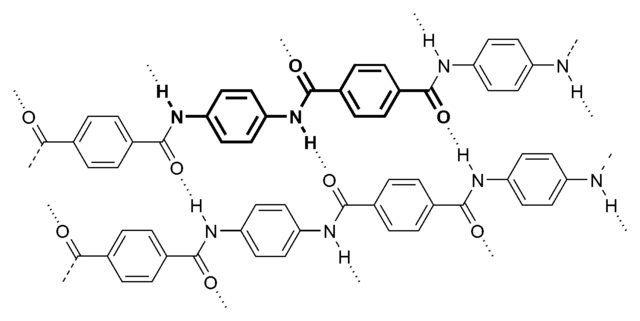
Aramid consists of relatively rigid polymer chains with linked benzene rigs and amide bonds. The structure endows aramid fibers with high tenacity, high modulus, and great toughness.
The molecular structure of aramids can be shown below:
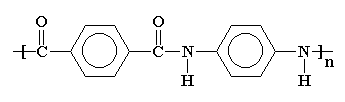
Aramid
Kevlar is a kind of polyamide. Its amide groups are separated by para-phenylene groups. The amide groups attach to the phenyl rings opposite each other, at carbons 1 and 4.
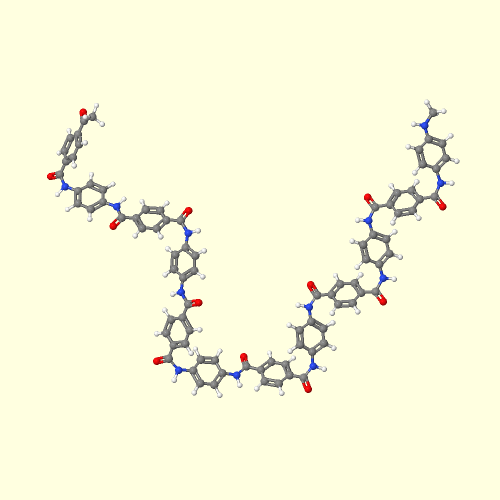
3D Model of Kevlar Aramid. Click Here to see.
While Nomex is a polyamide, it has meta-phenylene groups. That is, the amide groups are attached to the phenyl ring at carbons 1 and 3.
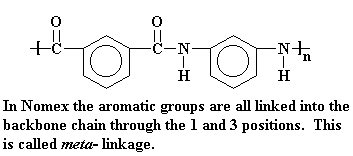
4. The Properties of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers are created with a range of impressive properties. But due to the differences between para-aramid and meta-aramid, here I'd list the two separately.
#1. Para-aramid (typical example: Kevlar)
√ High Strength-to-weight ratio: Para-aramid fibers, like Kevlar and Twaron, are slightly different from the others. The two have outstanding strength-to-weight properties. Plus, they have great tenacity, making it abrasion-resistant.
| Material | Strength-to-weight KN.m/kg. |
Ultimate Tensile Strength MPa |
Density g/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kevlar | 2514 | 2757 | 1.44 |
| Carbon Fiber | 2457 | 4137 | 1.75 |
| E Glass Fiber | 1307 | 3450 | 2.57 |
| Carbon Laminate | 785 | 1600 | 1.5 |
| E Glass Laminate | 775 | 1500 | 1.97 |
| Nylon | 69 | 75 | 1.15 |
√ High Young's Modulus (structural rigidity): 130-179 GPa. While carbon fiber is 300Gpa and glass 81GPa.
(Young's Modulus: Also known as elastic modulus. It defines the relationship between stress and strain in a material)
|
Material |
Young's Modulus GPa |
|---|---|
| Aramid(such as Kevlar and Twaron) | 70.5-112.4 |
| Nylon | 2-4 |
| Polypropylene | 1.5-2 |
√ Low elongation at break point, meaning that it stretches a little.
√ Para-aramids are usually Nonconductive under normal conditions.
√ Good Resistance to abrasion and cutting.
√ Good Resistance to organic solvents
√ Retain Low flammability, and are resistant to thermal degradation and self-extinguishing.
√ Keep Good fabric integrity at elevated temperatures
√ Excellent Dimensional Stability.
#2. Meta-aramid (typical example: Nomex)
√ Heat Resistance: Meta-aramid has long-lasting thermal stability. It can operate for long time at a temperature of 204°C and it maintains excellent dimensional stability. It doesn't go brittle, soften, or melt even if it is briefly exposed to temperatures up to 300°C.
√ Flame Resistance: Meta-aramid is inherently flame resistant. It won't self-burn or melt at regular levels of oxygen. And it's self-extinguishing. It will carbonize at 400°C.
√ Electrical Insulation: Meta-aramid has excellent electrical insulation properties. The dielectric strength of meta-aramid paper is up to 20kv/mm (Each meta-aramid differs).
√ Chemical Stability: Meta-aramid has a very stable chemical structure. It's resistant to organic solvents.
√ Radiation Resistance: Good resistance to Ultraviolet, α, and β.
√ Mechanical Properties: Meta-aramid is formable for moldable parts.
√ Low elongation at the breakpoint as well as para-aramid, meaning that it stretches a little.
The key properties of para-aramid and meta-aramid have been listed above. While the properties among para-aramid variations and meta-aramid variations differ, too.
The table below shows the various characteristics of aramid fibers and compiled from the Chemical Economics Handbook and Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, Vol.19 and Indian Journal of Fiber and Textile Research.
Properties of Commercial Aramid Fibers
|
Fiber Type |
Density g/cm3 |
Extension to Break % |
Modulus GPa |
Loop Elongation % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kevlar29 | 1.43 | 3.6 | 70 | 2.1 |
| Kevlar49 | 1.45 | 2.8 | 135 | 1.3 |
| Kevlar119 | 1.44 | 4.4 | 55 | 2.7 |
| Kevlar129 | 1.45 | 3.3 | 99 | |
| Kevlar149 | 1.47 | 1.5 | 143 | 0.6 |
| Nomex | 1.38 | 22 | 17 | |
| Twaron | 1.44 | 3.3 | 79 | |
| Twaron HM | N/a | 2 | 123 | |
| Technora | 1.39 | 4.3 | 70 | |
| Technora V106 | 1.32 | 3.7 | 77 |
5. Major Uses of Aramid Fibers
Thanks to the outstanding properties of aramid fibers, they can be used in a wide variety of industries.
√ Flame-resistant clothing: For example, military MIL-G-181188B suits. This includes Heat-protective clothing and helmets.
√ Substitute for asbestos (e.g. brake linings), whose fibers will give rise to pulmonary diseases after being inhaled into the lungs.
√ Hot air filtration fabrics
√ Reinforced thermoplastic pipes
√ Bullet-proof wear: Body armor, competing with PE-based fiber products such as Dyneema and Spectra.
√ Composite materials: Often combined with carbon fiber.
√ Tires, most recently as Sulfron (sulfur-modified Twaron)
√ Mechanical rubber reinforcement
√ Ropes and cables, although severely weakening under impact, limit their use on boats and climbing. Aramid cables are more applicable to static load situations; for example, the cables are used as guy-wires for hydro tower erection for Hydro Quebec.
√ Wicks for fire dancing
√ Optical fiber cable systems
√ Sailcloth (not necessarily racing boat sails)
√ Sporting equipment
√ Drumheads
√ Wind instrument reeds, such as the Fibracell brand
√ Loudspeaker diaphragms
√ Boat hull material
√ Fiber-reinforced concrete
√ Tennis strings (e.g. by Ashaway and Prince tennis companies)
√ Hockey sticks (normally in composition with such materials as wood and carbon)
√ Snowboards
√ Jet engine enclosures